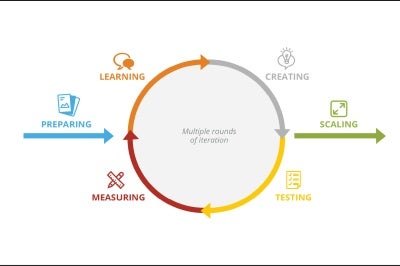
Customer experience projects gain momentum through swift cycles of investigation, creation, and testing. Whether a project takes a week or six months depends on the solution you envision and the scope of research and testing. Use timeline planning tools to launch the design, feedback, and refinement loop. Plan adequately and far in advance.
Dedicate no more than 2-3 weeks to each phase. Start by identifying a business challenge or opportunity and defining research objectives. Next, gather and analyze internal data and conduct customer research to gain insights; distill design principles and generate ideas; turn ideas into designs; test and prototype; gather feedback and adjust designs. Finally, launch a pilot, refine, and scale up.